Describe the Role of Prothrombin in Blood Coagulation
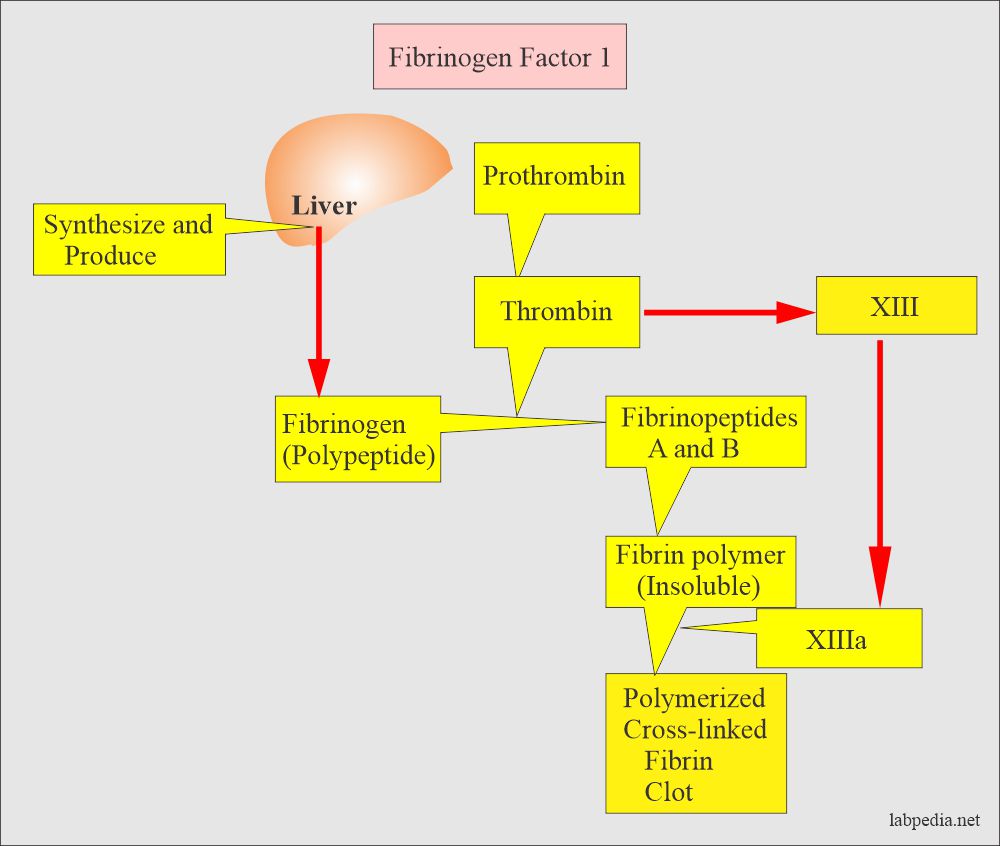
Fibrinogen originates from the liver and it is both intrinsic and extrinsic. An Arg-Thr bond gets cleaved releasing amino termial section and an Arg-Ile bond is cleaved opening a disulfide loob the resulting thrombin is actually a 2 chain molecule held together by a disulfide bond.
Blood Coagulation Factor And Interpretations
Distinguish how it is different from signal transduction in a s Distinguish how it is different from signal transduction in a s Q.

. It regulates its own generation by activating coagulation factors V VIII and. We have utilized two trauma patient databases database 1 n 358 and database 2 n 331 to investigate the. Blood coagulation is a system in which a series of zymogens of serine proteases are sequentially activated.
Long-term mechanism that triggers fibrin production Response of a capillary network to changing carbon dioxide levels Short-lived mechanism in which the damaged vessel dilates increasing blood flow and the amount of clotting agents at the site of the injury. Prothrombin is converted to thrombin by two hydrolyses. A method is described for the preparation and titration of prothrombin and thrombin.
Thrombin is a Na-activated allosteric serine protease of the chymotrypsin family central to blood coagulation with further involvement in inflammatory responses cell protection and apoptosis 123456. Hepperin is the anti coagulant to stop clotting internal or. Prothrombin factor 2 is present in blood.
In blood plasma have thrombin when bliding founds plasma come in contect of oxygen and prothrombin change in thrombin due to stimuli and fibrogen start coagulation and form a clot sheet on cut to protect from infection. The platelets or cephalin enormously accelerate the transformation of prothrombin to thrombin and this acceleration seems to be their physiological rôle in the coagulation process. Confirming the views of Morawitz Howell 1916-17 1925 and Bordet thrombin cannot be regarded as an artificial by-product of coagulation Wooldridge Nolf both quoted from Morawitz.
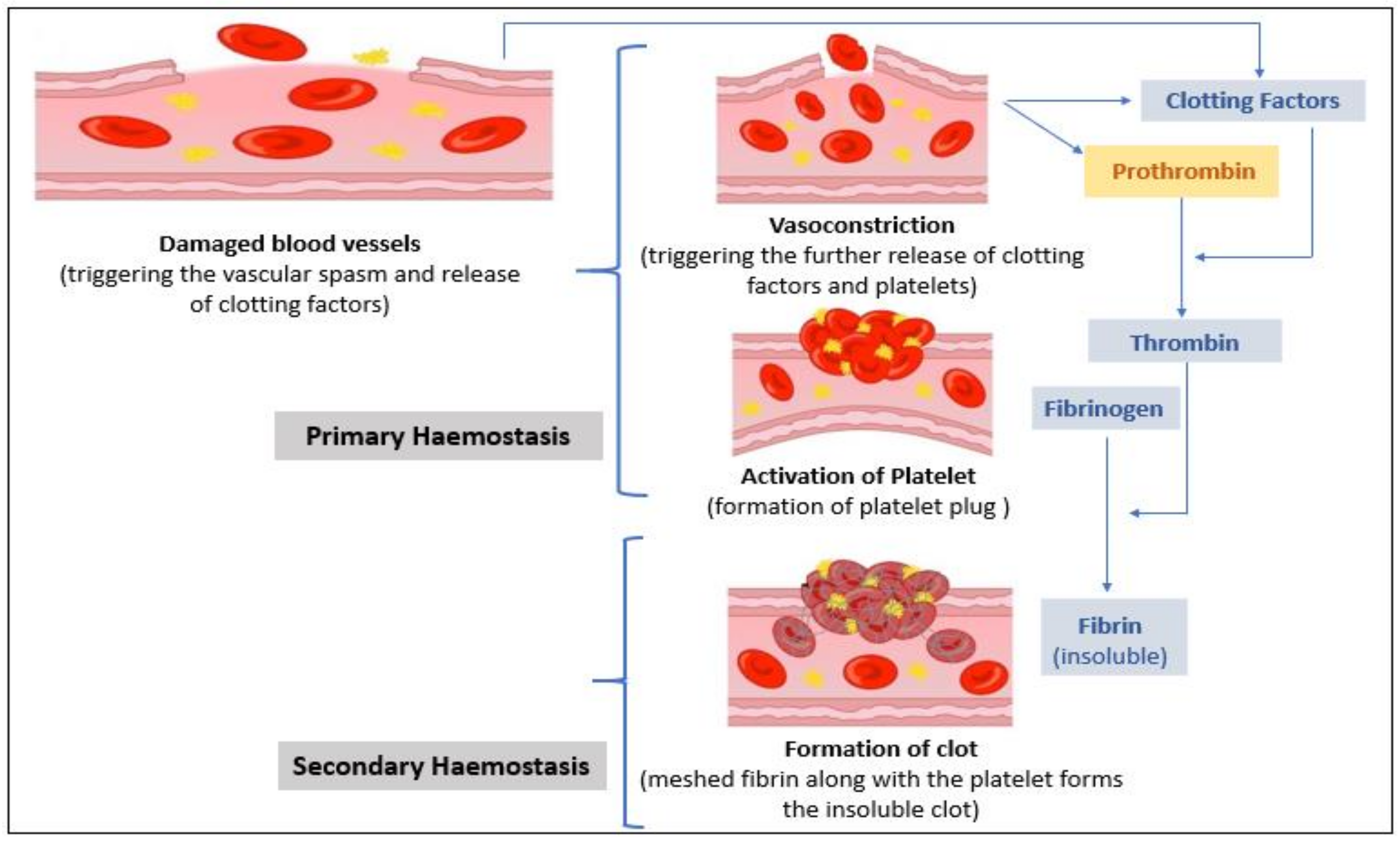
Describe how signal transduction occurs in Hearing ear. There are however several aspects unique to coagulation which are discussed in detail. The blood clotting process or coagulation is an important process that prevents excessive building in case the blood vessel becomes injured.
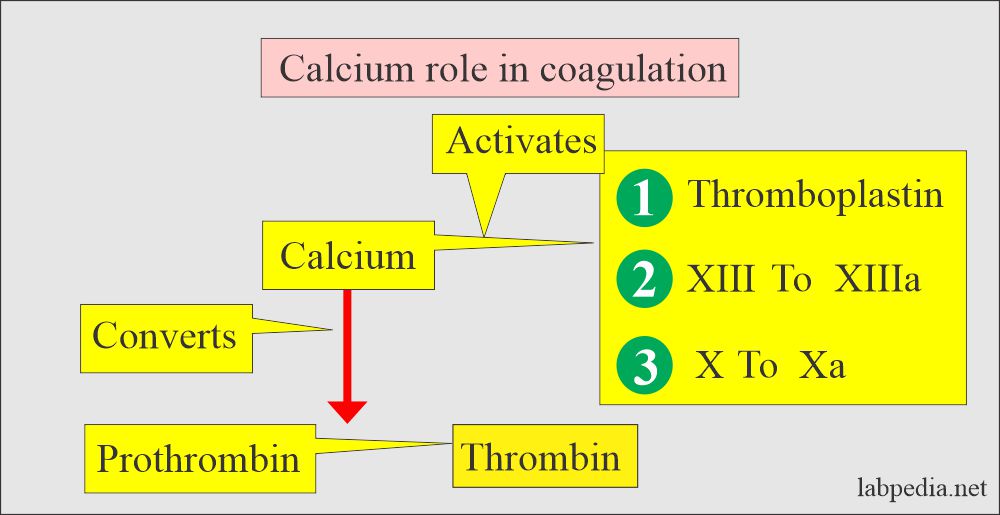
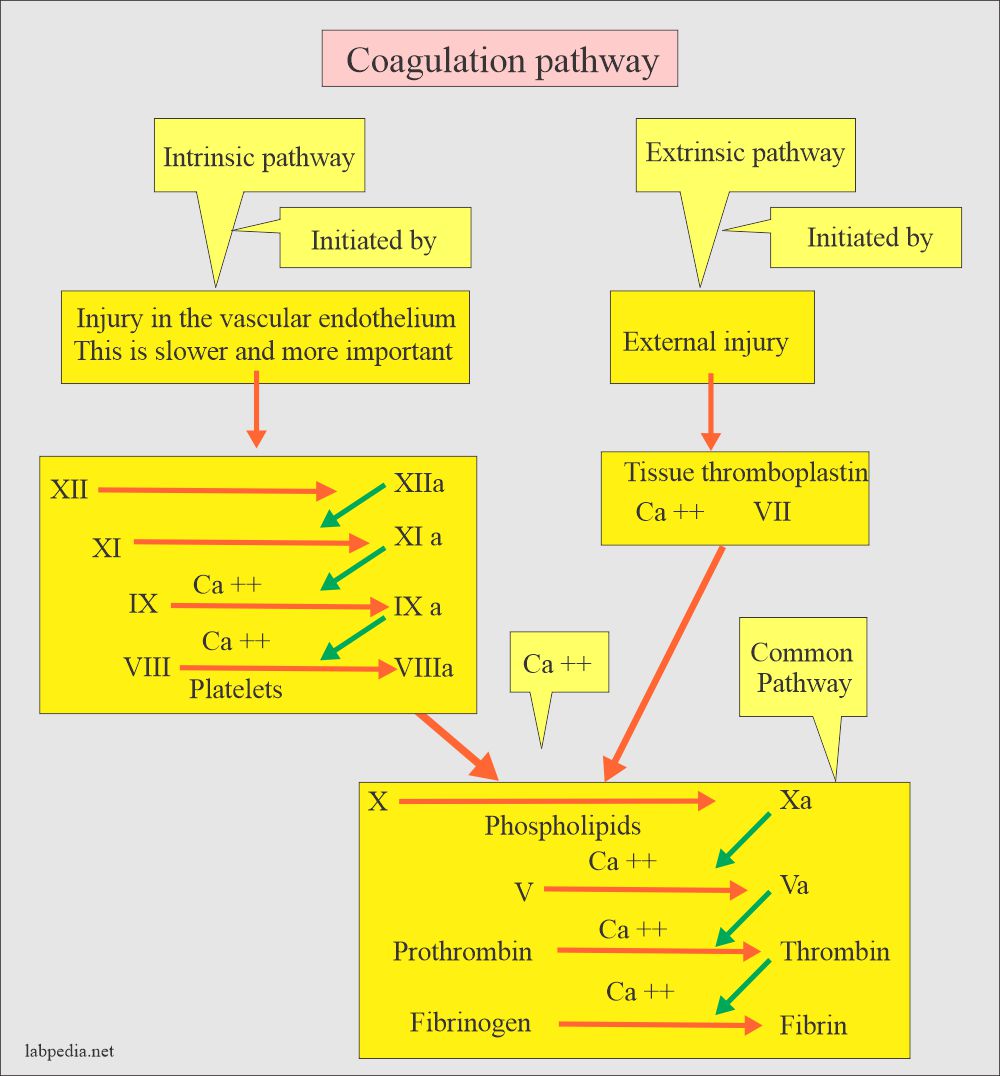
Initiate of intrinsic pathway and amplification of coagulation cascade small amounts of thrombin generated by the extrinsic pathway lead to activation of XI and XIa which initiates intrinsic pathway leading to amplification of coagulation in response to vascular injury. Thrombin then acts to transform fibrinogen also present in plasma into fibrin which in combination with platelets from the. Prothrombin activator in the presence of calcium factor V and phospholipids catalyzes the conversion of prothrombin to thrombin.
Prothrombin glycoprotein carbohydrate-protein compound occurring in blood plasma and an essential component of the blood-clotting mechanism. Describe a vascular spasm. Prothrombin is encoded by the coagulation factor II gene F2 which is located on chromosome 11p112 and is composed of 14 exons that encode a 622 amino acid preproprotein.
It has a high molecular weight and deficiency in Vitamin K or damage to the liver can disturb the blood. The human body protects against loss of blood through the clotting mechanism. Thrombin is an unique molecule that functions both as a procoagulant and anticoagulant.
Describe 5 stages in the Family Life Cycle and provide a realistic. It combines with thrombomodulin on endothelial cell surfaces to form a complex converting protein C to protein Ca Laposata M. Prothrombin is a 72 kDa single-chain protein containing ten gla residues in its N-terminal region.
Chemicals released from damaged blood vessels which initiate clotting by stimulating prothrombin activator Role of Prothrombin in clotting converted to thrombin in presence of Ca and prothrombin activator. Thrombin converts fibrinogen into fibrin which helps stop excessive blood loss by forming a mesh around the injured tissues. Expression of the F2 gene is exclusive to the liver.
Vascular mechanisms platelets coagulation factors. In your blood have some agents which are responsible to stop bleeding means repairs cuts. Conversion of prothrombin to thrombin.
In its procoagulant role it activates platelets through its receptor on the platelets. Prothrombin thrombin and fibrinogen are the main factors involved in the outcome of the coagulation cascade. In this regard there is little fundamental difference between coagulation and the activation of the homologous pancreatic zymogens.
Prothrombin is transformed into thrombin by a clotting factor known as factor X or prothrombinase. Fibrinogen and prothrombin have been suggested to become rate limiting in trauma associated coagulopathy. In addition to its role in the activation of fibrin thrombin also plays an important role in blood coagulation regulation.
Insoluble fibrin will be the end result when thrombin acts on soluble fibrinogen during the conversion process. Blood is a necessary component of the human body and the loss of this fluid may be life-threatening. Choose from 18 different sets of role of prothrombin in blood coagulation flashcards on Quizlet.
Administration of fibrinogen is now recommended however the importance of prothrombin to patient outcome is unknown. Learn role of prothrombin in blood coagulation with free interactive flashcards. Thrombin acts as an enzyme that cleaves fibrinogen into sticky and insoluble fibrin monomers.
Prothrombin is a plasma protein found in the blood that is continuously formed by the liver. Prothrombin and fibrinogen are proteins that are produced and deposited in the blood by the liver. Each of the clotting factors has a very specific function.
Blood is generated via hematopoiesis and ultimately becomes the delivery method for oxygen to the tissues and cells. The amount of thrombin formed in a mixture of prothrombin Ca and platelets is independent of the platelet or Ca concentration and depends primarily upon the amount of prothrombin used.
Blood Coagulation Factor And Interpretations

Blood Clotting Pathway Prothrombin Thrombin Vitamin K Adds Gcoo To Glutamate Of Prothrombin Also Vii Ix X Coumadin Inhibits Vit K Action Ppt Download

Hemostasis And Blood Coagulation Blood Cells Immunity And Blood Coagulation Guyton And Hall Textbook Of Medical Physiology 12th Ed

Secondary Hemostasis Biochemistry Notes Medical Studies Hematology
Sensors Free Full Text Evolving Paradigm Of Prothrombin Time Diagnostics With Its Growing Clinical Relevance Towards Cardio Compromised And Covid 19 Affected Population Html
Blood Coagulation Factor And Interpretations
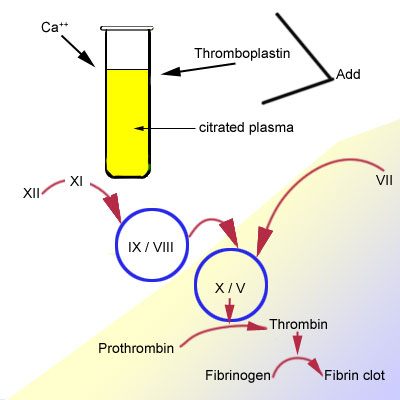
Blood Laboratory Hemostasis Pt And Ptt Tests

3 Key Components Of The Coagulation Cascade Calcium Ions Which Are Required For Several Key Reaction Steps Coagulation Fa Physiology Mcat Study Biochemistry

Activated Partial Thromboplastin Time Aptt Prothrombin Time Pt Download Scientific Diagram
What Are The Similarities Between Intrinsic And Extrinsic Pathways Of Blood Coagulation Quora

General Approach In Investigation Of Hemostasis Ppt Download Prothrombin Time Disseminated Intravascular Coagulation Test Tube

Coagulation Clotting Mechanisms Circulatory System Mcat Content

Bleeding And Blood Clotting Intrinsic Pathway Of Blood Coagulation Britannica

Simplified Scheme Of Blood Coagulation Reactions Exposure Of Tissue Download Scientific Diagram

The Coagulation Cascade Medical Laboratory Science Medical Science Medical Technology

Question Video Explaining The Role Of Thrombin In Blood Clotting Nagwa

Hemostasis Lesson 4 Tests Inr Ptt Platelets Fibrinogen D Dimer D Dimer Medical Lab Technician Cardiac Nursing

Question Video Explaining The Role Of Thromboplastin In Blood Clotting Nagwa

Comments
Post a Comment